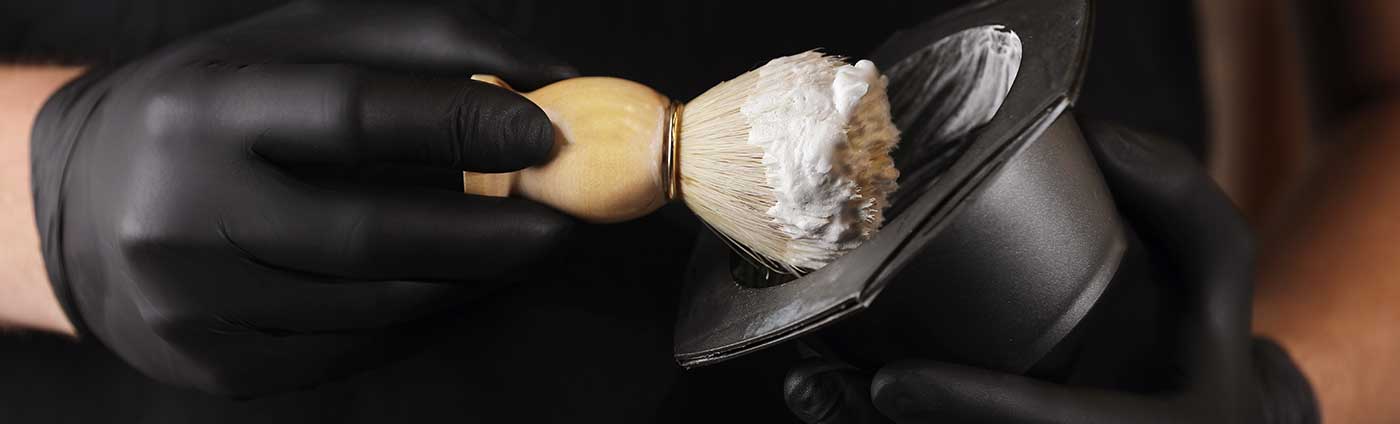
One of the most important elements of a wet shave is good foaming. A thick, dense, rich, smooth… mmm, sorry, lost my train of thought for a sec, anyway, a rich foam makes a big difference in the comfort and efficiency of your shave.
Shaving Cream and Shaving Soap both have their advantages and disadvantages. Shaving cream is typically more expensive than shaving soap, but it can be worth the investment because it provides a closer shave. Shaving Cream is also easier to apply than shaving soap and doesn’t require a brush. However, some men prefer shaving soap because it produces a richer lather. Shaving soap also has the advantage of lasting longer than shaving cream.
But What’s The Difference Between Shaving Cream And Soap?
Shaving Cream is typically made with a combination of oils, water, and emulsifiers. This combination helps to soften the hair and create a smooth surface for the razor to glide over. Shaving soap, on the other hand, is made with saponified oils (oils that have been turned into soap). This type of soap can be quite drying, so it’s important to choose one that includes some moisturizing ingredients.
Both shaving cream and shaving soap can provide a close shave. However, many people find that shaving cream is more comfortable to use and leaves their skin feeling softer and smoother.
Shaving Cream
Shaving cream is a thick, creamy substance that is used to lubricate the skin and hair during shaving. It helps to reduce friction and irritation, making the process of shaving much more comfortable. Shaving cream also has a number of other benefits, including providing a close shave, hydration, and protection from razor burn.
So what exactly is in shaving cream that makes it so beneficial? Most formulas contain a combination of oils, emollients, and humectants. These ingredients work together to soften the hair and provide slip, so that the razor can glide smoothly over the skin.
Shaving cream can be applied in a number of ways, but the most common is to simply lather it onto wet skin with your hands or a brush.
Shaving cream is a necessary part of the shaving process for many people. It lubricates the skin and hair, making it easier to shave without irritation. There are many different types of shaving cream available on the market, and each one has its own unique ingredients.
The most basic type of shaving cream contains only a few simple ingredients. Water makes up the majority of the product, while lubricating agents like glycerin help to reduce friction. Thickening agents like sodium laureth sulfate give the shaving cream its creamy texture, while preservatives help to extend its shelf life.
Some shaving creams also contain additional fragrance or menthol to provide a refreshing sensation during use. These ingredients are generally considered safe for most people, but those with sensitive skin may want to avoid them. There are also some organic and natural options available that use only safe, gentle ingredients.
Ingredient Usually Found Only In Shaving Creams
Myristic Acid: Is an organic fatty acid formed from the saponification of coconut oil (acid). This surfactant can help accelerate foaming and, like water, has excellent emulsifying properties, so it will give a very stable foam with all saponification and botanical ingredients. Evenly distributed. This is not found in appreciable concentrations in many hard soaps or cream soaps.
Methylchloroisothiazolinone: is an ingredient commonly used to preserve various products, such as moisturizing lotions and shaving shaving creams. This substance is effective against fungi and bacteria, but is also known to cause minor skin irritation in those who are already sensitive or already have an allergic reaction to it.
Shaving Soap
Shaving soap is a type of soap that is designed specifically for shaving. Unlike regular bar soap or body wash, shaving soap is made with ingredients that help to soften the hair and provide a close shave. Shaving soap is often made with glycerin, which helps to create a lather that is both thick and creamy.
If you are new to shaving, or if you have never used shaving soap before, it is important to know how to use it properly. Wet your face with warm water and apply the shaving soap to your wet skin. Use a brush or your fingers to work the soap into a lather. Apply the lather to your beard or mustache area and shave as usual. Rinse your face with cold water when you are finished.
Shaving soap is a type of soap that is designed specifically for use on the face to shave hair. It is usually made with a variety of different oils and fats that help to create a rich, creamy lather that can help to soften the hair and make it easier to shave. There are a number of different ingredients that can be used in shaving soap, but some of the most common include:
Coconut oil: This oil is often used as the base for shaving soap as it helps to create a thick, creamy lather. It also has natural antibacterial properties that can help to keep the skin clean and free from infection.
Olive oil: Another popular option for the base of shaving soap, olive oil helps to create a similar rich lather while also providing some moisturizing benefits.
Ingredients Typically Found Only In Soap
Tallow: This is a fatty acid derived from bovine, obtained by steam fusion of the original solid fat. The less dense and less soluble animal fat sits on top of the denser fat and is collected. Mallow is usually mixed with coconut acid / oil and then saponified.
When water is added to the soap through the dilution process, the tallow gives the foam an incredible softness. Since soap is obtained after saponification of this ingredient, tallow is used almost exclusively in soaps.
Jojoba: The jojoba oil is derived from the seeds of the jojoba plant (S. chinensis) and is virtually unsaponifiable. This means that it will not contribute in soap production and have a non-solid physique. Jojoba oil is very similar in function and molecular structure to sebum, a natural substance in the skin. People with very dry skin will find this ingredient especially helpful in terms of the “post-shave feel”. Together with glycerin, this will keep the skin very soft and hydrated.
Shea Butter: Derived from the African shea tree, many of the unsaponifiable substances of shea butter are used in shaving soaps. Triterpene alcohol makes up most of the shea butter obtained. In this alcohol is a “cinnamate ester” that has such a high UV protection rate that it is used in many advanced and highly protective sunscreens. Along with jojoba oil, shea butter is also very helpful in retaining moisture in the skin and helping the skin quickly return to its normal hydrated state.
Shaving Cream And Soap
In addition, ingredients may be added to both soap and shaving creams to improve certain properties. You’ll often find glycerin, shea and other butters, jojoba oil, bentonite clay and lots of other additives that help promote hydration, create a behind-the-surface feel, stable lather and more. More products can be added to contribute to the post-shave facial feel and visibly nourished skin. They can be vegan and created only with products of plant origin.
- Creams and soaps have a wonderful, long-lasting scent.
- Shaving cream and shaving soap can be evenly mixed with a quality shaving brush.
- It helps to dissolve many ingredients used in shaving creams/soaps. As a “wet” agent in wet scraping, it is especially useful when added during milling due to its excellent emulsifying properties.
- The water content plays an essential role in determining the final consistency of a product during the manufacturing process.
Stearic Acid: Very important for saponification – or, soap making. This saturated fatty acid is an organic (carbon-containing) triglyceride that combines with another ingredient to form a soap/cream. It is also known as a surfactant, or a substance that reduces the surface tension between itself and other liquids or solids. This will help “slide” the foam.
Sodium / Potassium Hydroxide: These inorganic molecules are another very important ingredient for making the base of shaving soaps/shaving creams. Sodium hydroxide is used as the primary substrate and in the highest concentrations when a soap/”croap” consistency (a combination of cream and soap) is desired, although it is always found in lower concentrations in lotions and shaving creams.
Potassium hydroxide: is used as the main saponifying agent in creams. When either hydroxide is introduced into solution, it ionizes into its main components: sodium/potassium and the hydroxide group. The hydroxide group will remove a hydrogen atom from the so-called “carboxyl” end of stearic acid, as well as (in the correct concentration) from any other organic acids/oils/butters present.
After saponification, you will have formed a carboxylate functional group. This is where you get potassium or sodium stearate/cocoate/butterate, etc. All of these “eatens” are basic and will be quite slippery.
Side Note: By their very nature, bases attract and can “steal” hydrogen ions, usually other water molecules. This is why some people may find their skin a bit tight after shaving, as primer can make the skin indiscriminately more basic than it would be without removing makeup.
**Concentrations and ratios of these ingredients are important for maintaining skin stability. soap pH. Too low or too high, the soap/cream may degrade.
Glycerin: Glycerin is a great addition to soaps and shaving creams. It can be added, but it is created during the actual saponification process. Glycerin has effective moisturizing properties, which means it holds water very well. This will greatly help with water retention and foam stability. Glycerin is also easily absorbed by the epidermis of the skin and, thanks to its moisturizing properties, gently attracts and holds water in the epidermis, keeping the skin hydrated.
Glycerin can also contribute to the mildness of soaps and shaving creams.
Whether you’re new to wet shaving or experienced shaving, shaving cream or shaving soap can provide the lubricating lather you’re looking for for a perfectly smooth face.
Which One Is Better? Shaving Cream Or Soap?
When it comes to finding the perfect shaving solution, there are two main options – shaving soap or shaving cream. Both have their own benefits and drawbacks, but when it comes down to it, shaving cream is the better option. Here’s a comparison of the two to help you make the best decision for your own shave.
Shaving cream is a newer invention but has quickly become a popular choice for its many benefits.
Shaving cream is generally more expensive than soap, but it is worth the extra cost. Shaving cream provides a protective barrier between your skin and the razor, resulting in a closer shave with less irritation.
Shaving soap can be harsh on your skin, especially if you have sensitive skin. It can also cause razor burn and ingrown hairs. Shaving cream contains moisturizers that help to protect your skin and prevent these issues.
Shaving soap has been around for centuries and was the traditional choice for many years. It’s easy to find and relatively inexpensive, which makes it an attractive option for many people. However, soap can be harsh on the skin and doesn’t provide as much lubrication as shaving cream does. This can lead to razor burn, nicks, and cuts.
In conclusion, shaving cream is the better choice for most people.







More Stories
Men’s Face Washing Guide
In the ever-evolving world of men’s grooming, a solid skincare routine is the foundation of
Jan
How To Shave With A Straight Razor
There’s something about shaving with a straight razor that feels manly. It’s the same razor
Aug
Chemical Properties Of Shaving Cream
We know that men have many questions about shaving cream benefits, properties, and functionality, we
Jul